Introduction
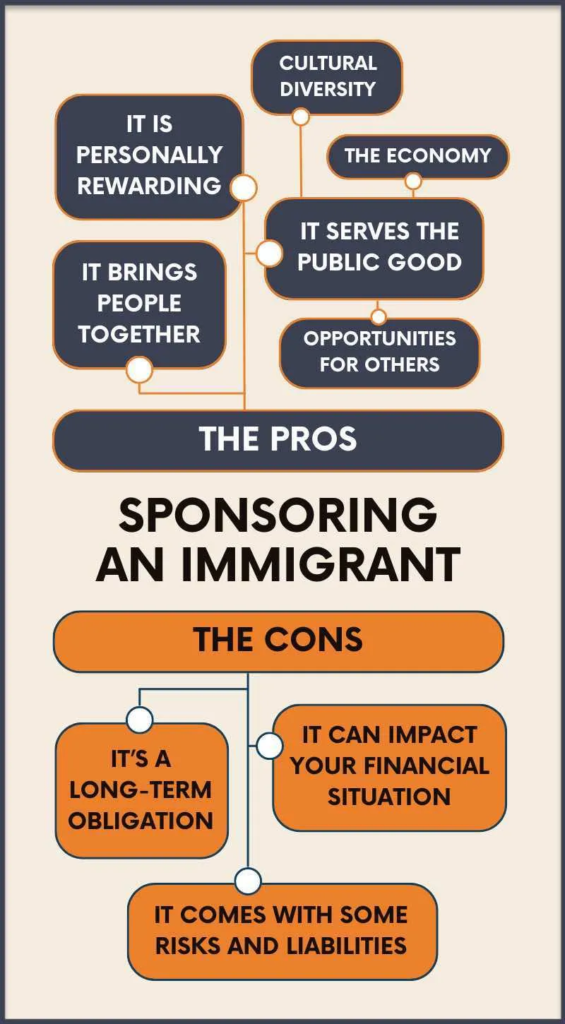
Visa sponsorship is an essential process for individuals looking to work, study, or live in a foreign country. For many, securing a visa sponsorship is one of the primary obstacles in obtaining permission to enter a foreign country. But who can provide visa sponsorship, and what are the criteria and responsibilities involved? This article will explore the entities and individuals who are able to provide visa sponsorship, the different types of visas, and the legal requirements associated with the sponsorship process.
You May Also Like:
1. What is VISA Sponsorship?
Visa sponsorship is the process by which an individual or an organization agrees to support a foreign national’s application for a visa. It typically involves guaranteeing that the visa applicant will adhere to the rules of the visa and, in some cases, ensuring they have the financial means to support themselves during their stay. Visa sponsorship is commonly required for work, student, and family-based immigration.
For example, in the United States, the U.S. employer might sponsor a foreign worker for an H-1B visa, allowing the worker to live and work in the U.S. legally. In contrast, a university may sponsor a student for an F-1 visa to study in the U.S.
2. Who Can Provide VISA Sponsorship?
Various entities can provide visa sponsorship, including government bodies, private companies, educational institutions, and sometimes individuals, depending on the country and type of visa. Here’s a breakdown of the main types of sponsors:
a. Employers and Companies
The most common visa sponsors are employers and businesses. Companies that wish to hire foreign workers are responsible for providing visa sponsorship, especially for work-related visas.
Employer-Sponsored Visas: Many countries, including the U.S., Canada, and the UK, allow employers to sponsor foreign workers for employment-based visas. Examples include:
- H-1B Visa (U.S.): An employer sponsors a worker for a temporary job in a specialty occupation, typically requiring a bachelor’s degree or higher.
- Skilled Worker Visa (UK): Employers in the UK can sponsor workers from outside the EU who meet specific job skill requirements.
- Temporary Work Visa (Australia): Employers can sponsor workers for temporary positions in fields experiencing labor shortages.
The sponsoring employer must prove that the foreign national meets the qualifications for the position and that no qualified local workers are available for the job. This involves a substantial amount of paperwork and can be costly for the employer.
b. Educational Institutions
Students often require visa sponsorship to study abroad, and in many cases, educational institutions provide that sponsorship. For instance, universities, colleges, or even language schools in various countries may sponsor students for study visas.
Student Visas: Countries with high numbers of international students—like the United States, the UK, Australia, and Canada—have structured visa programs specifically for academic purposes. These institutions are responsible for providing students with the necessary documentation to apply for their student visa.
Student Visa Sponsorship Process: Typically, a student must apply and be accepted into a recognized institution before they can receive sponsorship. Once the acceptance is granted, the institution issues a certificate of enrollment, which the student then submits as part of their visa application.
c. Government Agencies
In some cases, government programs and public sector organizations can also provide visa sponsorship, particularly in programs where a country is seeking to attract skilled workers, researchers, or entrepreneurs.
Government-Sponsored Programs: Countries like Canada and Australia offer immigration programs that encourage foreign nationals to move to the country for employment or entrepreneurship purposes. These governments often sponsor individuals who meet specific criteria in high-demand fields.
- Canada Express Entry: The Canadian government has a program that allows individuals to apply for permanent residence, including through employer sponsorship.
- Australia’s Skilled Migration Program: This program offers sponsorship for skilled workers based on the demand for specific occupations within the country.
These programs typically involve a points-based system, where points are awarded based on qualifications, work experience, language proficiency, and other factors.
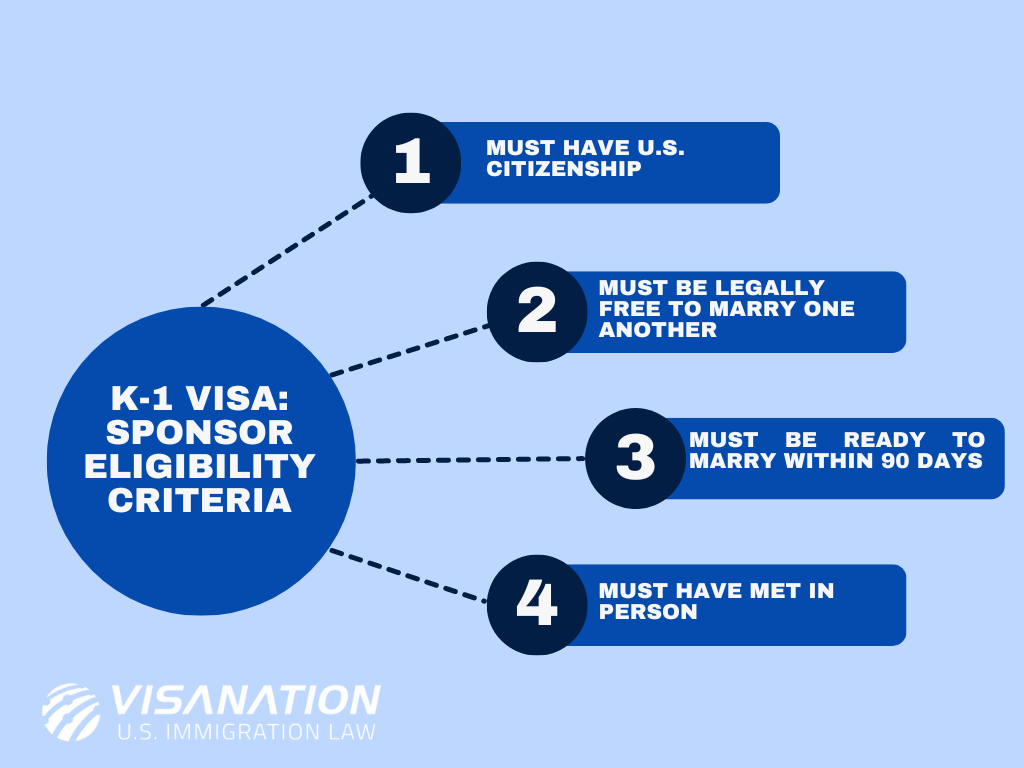
d. Family Members
Some countries allow individuals to sponsor their relatives for visa purposes. This type of sponsorship is generally seen in family reunification programs and is often available for spouses, children, and in some cases, extended family members.
Family-Sponsored Visas: In countries like the United States, Canada, and the UK, citizens and permanent residents can sponsor certain relatives to come and live with them. While this is often the most straightforward path for family members, the process can still be long and complicated. The sponsor must prove their relationship and demonstrate financial stability to support the relative.
Examples of family-sponsored visas include:
- Family Reunification (U.S.): U.S. citizens can sponsor spouses, children, and other immediate family members for visas.
- Parent or Spouse Visa (Australia): In Australia, citizens and permanent residents can sponsor their spouses or parents for residency.
e. International Organizations and Non-Profits
In some instances, non-governmental organizations (NGOs) and international institutions such as the United Nations, the World Bank, or similar organizations provide visa sponsorship for specific projects, humanitarian work, or volunteer programs.
These entities might sponsor individuals for both short-term and long-term stays, depending on the project or initiative. Volunteers, researchers, and individuals with specialized skills in areas like healthcare, education, and the environment can often receive sponsorship under these conditions.
3. Types of VISA Sponsorships
Visa sponsorships come in various forms, each tailored to specific purposes. Some of the most common types of visa sponsorship include:
- Work Visas: For individuals coming to work in a specific job or occupation. These visas are typically employer-sponsored and require the employer to prove that no local workers are available for the position.
- Student Visas: Sponsored by educational institutions, allowing foreign nationals to study at universities, colleges, or schools in the host country.
- Family Visas: Sponsorship provided by a family member to bring relatives into the country for long-term or permanent residence.
- Entrepreneur and Investor Visas: Sponsored by individuals who plan to invest in a business or create one in the host country.
- Exchange Visitor Visas: These are usually sponsored by institutions or organizations that have cultural exchange programs, such as research programs or fellowships.
4. Responsibilities of the VISA Sponsor
The sponsor has legal and financial responsibilities during the visa process and for the duration of the visa holder’s stay. Depending on the type of visa, these obligations can include:
- Financial Support: The sponsor may need to prove their ability to financially support the visa holder during their stay, ensuring the applicant does not rely on public funds.
- Legal Compliance: Sponsors must ensure the visa holder complies with all local laws and visa conditions, including working within the allowed hours or maintaining full-time enrollment in a school.
- Providing Documentation: The sponsor must submit necessary documents to government agencies and cooperate with any required legal processes, such as providing updates on the visa holder’s status.
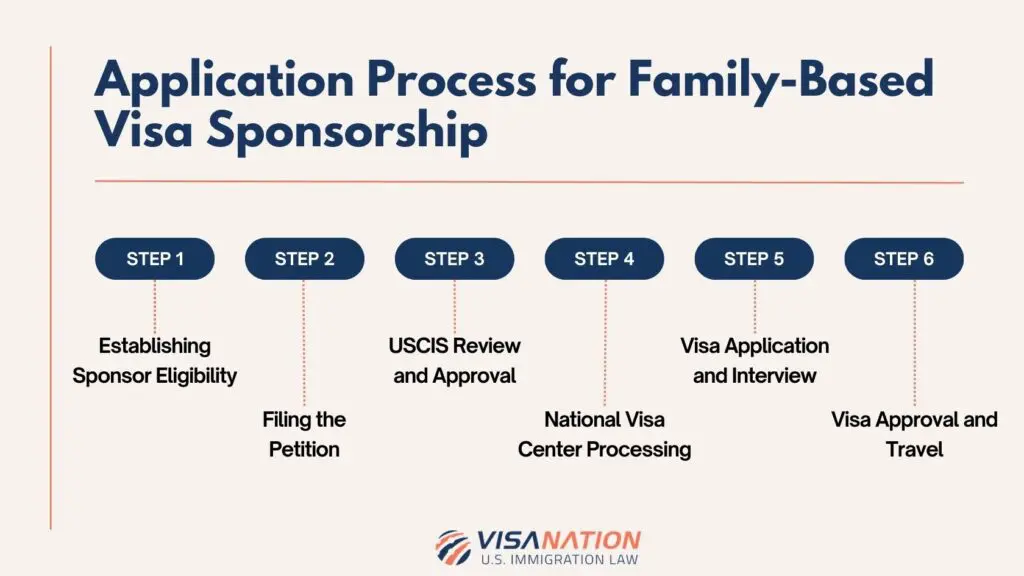
5. The Application Process for VISA Sponsorship
The process of securing visa sponsorship typically involves multiple steps:
- Identify the Type of Visa: Understand the specific visa requirements for the country and type of sponsorship.
- Find a Sponsor: This could mean finding a job, being accepted into a school, or having a family member who is eligible to sponsor you.
- Submit Documentation: The sponsor and applicant must gather necessary documents (e.g., job offers, financial proof, academic transcripts).
- Apply for the Visa: Submit the completed application to the appropriate immigration authorities.
- Attend Interviews (if required): Depending on the country and type of visa, interviews may be part of the process.
- Wait for Approval: The approval process can vary by country, with some taking several weeks or months.
6. Challenges in Securing VISA Sponsorship
While many people successfully secure visa sponsorship, it is not without challenges. Some of the most common challenges include:
- High Competition: Countries with limited visa quotas, such as the U.S. for H-1B visas, often see intense competition, making it difficult to secure sponsorship.
- Strict Eligibility Requirements: Some visa types require specific qualifications, experience, or documentation, which may be difficult for some applicants to meet.
- Lengthy Processing Times: The application process can take months, creating delays that may affect an individual’s ability to start a job or study program on time.
- Financial Burden: Visa sponsorship often involves substantial costs for the sponsor, including legal fees, application fees, and the financial responsibility of supporting the visa holder.
7. Key Considerations When Seeking VISA Sponsorship
When applying for visa sponsorship, both the applicant and the sponsor should be aware of several important factors that could affect the process. Understanding these factors can help avoid complications and ensure that the application is processed efficiently.
a. The Sponsorship Timeline
The timeline for securing visa sponsorship can vary significantly depending on the country, type of visa, and specific circumstances. For instance, employer-sponsored visas like the H-1B in the United States have annual application windows, and candidates are subject to a lottery system due to high demand. On the other hand, family-sponsored visas may take several months or even years to process, especially if there is a backlog in the immigration system.
It’s important for both the applicant and sponsor to plan ahead and be patient. Applicants should be prepared for potential delays and ensure they have all required documentation ready in advance. Sponsors should understand the processing time associated with their specific type of sponsorship and communicate this to the applicant clearly to avoid misunderstandings.
b. Visa Sponsorship Fees
Visa sponsorship is often accompanied by significant fees, both for the sponsor and the applicant. These costs can vary depending on the type of visa and the country in which the application is being processed.
- Application Fees: Many countries charge application fees that must be paid when submitting the visa application. These fees can range from modest amounts to several hundred dollars, depending on the visa type.
- Legal Fees: In some cases, especially for employer-sponsored visas, the employer may need to hire legal professionals or immigration consultants to navigate the application process. These legal fees can add up, particularly if the visa process involves a lot of paperwork or complex regulations.
- Health Insurance and Support Costs: Some countries require that applicants have health insurance for the duration of their stay. In addition, sponsors may need to demonstrate that they can financially support the applicant, ensuring they don’t become a public charge.
It is important to budget for these costs early on, as they can be substantial, particularly for employer-sponsored visas or family-sponsored immigration. Applicants should also be aware of any additional costs they might incur for things like medical exams, document translation, or travel.
c. The Role of the Sponsor’s Reputation
The credibility and reputation of the sponsor, particularly in the case of employer-sponsored or academic sponsorships, play a significant role in the success of the application. Immigration authorities scrutinize the sponsor’s background to ensure they meet the legal and financial requirements to sponsor a foreign national.
For employers, this means maintaining a strong record of compliance with immigration laws, labor regulations, and fair hiring practices. For educational institutions, it means ensuring that the school is accredited and able to support the international student throughout their studies.
Family sponsorships generally require the sponsor to demonstrate financial stability and proof of a genuine family relationship. In some cases, the sponsor may also be required to prove that they will provide adequate accommodation and support for the visa holder.
d. The Sponsor’s Ability to Fulfill Obligations
The sponsor has a legal responsibility to fulfill certain obligations during the applicant’s stay in the country. For employers, this may involve ensuring that the employee is paid according to the terms of the visa, providing the agreed-upon benefits, and adhering to labor laws. Employers may also be required to notify immigration authorities if the worker’s status changes or if they fail to comply with the conditions of their visa.
For family members sponsoring relatives, the sponsor must prove that they have sufficient financial means to support their relative, ensuring that the visa holder does not rely on public assistance.
These responsibilities highlight the importance of selecting a reliable sponsor who can fulfill these obligations, as failure to do so could jeopardize the applicant’s visa status and lead to legal consequences.

You May Also Like:
8. Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
While the visa sponsorship process is designed to facilitate international mobility, there are several challenges that applicants and sponsors might encounter. Below, we examine some common issues and provide strategies to overcome them.
a. Limited Availability of Sponsorship Opportunities
One of the most common challenges when seeking visa sponsorship is the limited number of spots available, especially for work or employment-based visas. For example, in countries like the United States, the H-1B visa program has an annual cap, and many applicants may be left out of the process due to a lottery system or lack of available spaces.
Solution: Applicants should focus on developing skills that are in high demand in the target country. For example, fields like technology, healthcare, and engineering are often more likely to have available sponsorship opportunities. Additionally, applicants can explore alternative visa categories, such as those for entrepreneurs, investors, or researchers.
b. Navigating Complex Legal Requirements
Visa sponsorship often involves navigating complex legal requirements, including ensuring that both the sponsor and the applicant meet all eligibility criteria. The sponsor may need to submit various forms, pay fees, and provide detailed documentation to prove the applicant’s qualifications, intent, and ability to comply with immigration laws.
Solution: Applicants and sponsors should seek professional legal advice or hire immigration consultants to help navigate the legal landscape. Working with experts can reduce the risk of mistakes, delays, and rejections.
c. Meeting Financial Requirements
One of the key requirements for visa sponsorship is the ability to support the applicant financially. Sponsors, especially in the case of family and student visas, must provide evidence of their financial ability to cover the visa holder’s living expenses, healthcare, and other needs.
Solution: Sponsors should ensure they can meet the financial requirements before beginning the sponsorship process. This might involve providing tax returns, bank statements, or affidavits of support that demonstrate financial stability. In the case of employment-based visas, employers need to show that the position offers a salary that meets minimum wage laws and is sufficient to support the employee.
d. Long Waiting Times and Delays
Visa applications, especially for countries with high demand for foreign workers or students, can experience long processing times. Applicants might face uncertainty and frustration as they wait for their visa to be approved.
Solution: While waiting for a visa decision can be stressful, applicants should ensure that they submit their applications as early as possible. If the process is taking longer than expected, applicants should contact the relevant authorities to check on the status of their application and confirm that no additional information is needed.
9. Conclusion
Visa sponsorship plays a crucial role in facilitating international mobility, whether for work, study, or family reunification. Employers, educational institutions, government agencies, family members, and non-profits all play an important part in this process. While securing a visa sponsorship can be challenging, it remains a vital pathway for many individuals looking to live and work abroad. Understanding the responsibilities and requirements involved in obtaining visa sponsorship is essential for both applicants and sponsors to ensure a smooth application process.